What is DevOps?
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
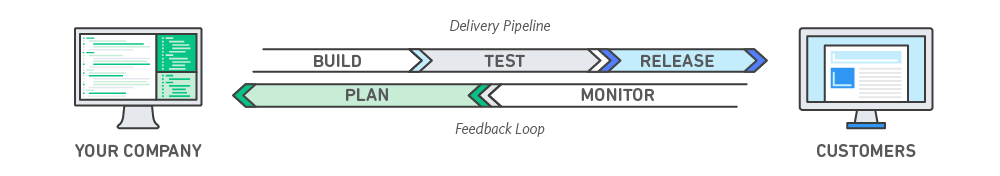
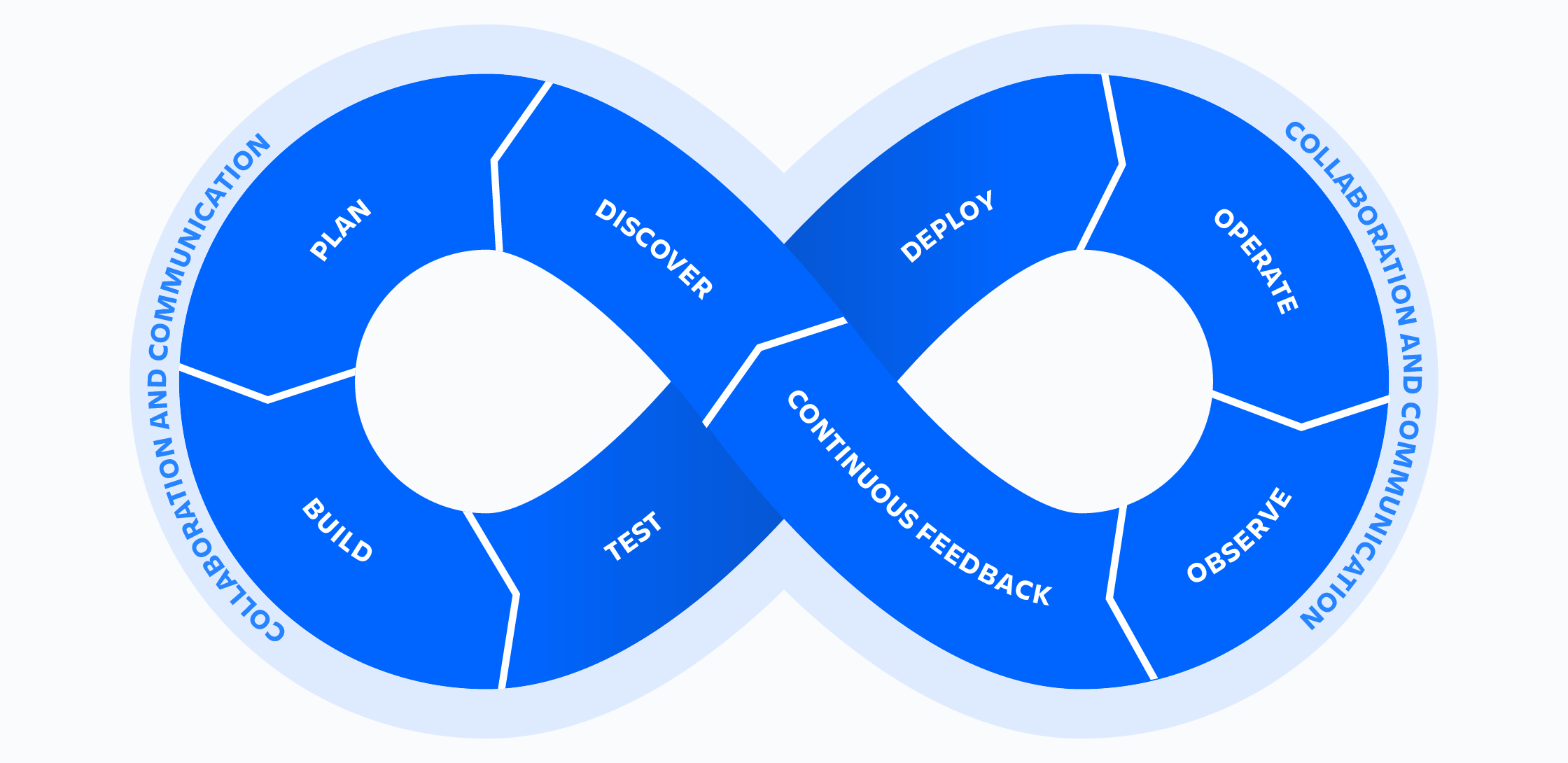
How does DevOps work?
A DevOps team includes developers and IT operations working collaboratively throughout the product lifecycle, in order to increase the speed and quality of software deployment. It’s a new way of working, a cultural shift, that has significant implications for teams and the organizations they work for.
DevOps teams use tools to automate and accelerate processes, which helps to increase reliability. A DevOps toolchain helps teams tackle important DevOps fundamentals including continuous integration, continuous delivery, automation, and collaboration.
Before DevOps Vs After DevOps Implementation
| Before DevOps | After DevOps |
|---|---|
| Miscommunication Between Dev and Ops Teams | Improved Collaboration |
| Absence of DBAs in Release Cycles | Collaborative Customer Feedback and Optimization |
| Haphazard Code Execution | Speedy Execution |
| Delayed Software Deployments | Rapid Delivery |
| Constant Monitoring of Application Maintenance and Performance | Sustained Software Development |
| Operational Costs | Reduced Costs |
| Lack of Scope for Innovation | Improved innovation |
| Low Failure Recovery Rate | Reduced outages |
| No scope for Continuous Integration | Continuous Integration |